On this animated GIF, the clouds on the periphery of a few of Jupiter’s polar cyclones spin counterclockwise whereas the core of the cyclones spin clockwise. The JunoCam pictures used for this animation had been captured from heights of roughly 28,567 kilometers above Jupiter’s cloud cowl. Citizen scientist Gerald Eichstädt processed the photographs to enhance shade and distinction. Picture data: NASA / JPL-Caltech / SwRI / MSSS. Picture processing: Gerald Eichstädt © CC BY
The spaceship has been accumulating data concerning the inside of the gasoline large since July 2016. A few of his newest discoveries concern “sizzling spots” within the planet’s environment.
Twenty-five years in the past NASA despatched the primary probe in historical past into the environment of the biggest planet within the photo voltaic system. However the info that the Galileo probe returned throughout its descent into Jupiter triggered head scratches: the environment it was immersed in was a lot denser and hotter than scientists anticipated. New data from NASA’s Juno spacecraft counsel that these “sizzling spots” are a lot wider and deeper than anticipated. The outcomes on Jupiter’s hotspots and an replace on Jupiter’s polar cyclones had been introduced on December 11, 2020 throughout a digital media briefing on the American Geophysical Union’s autumn convention.
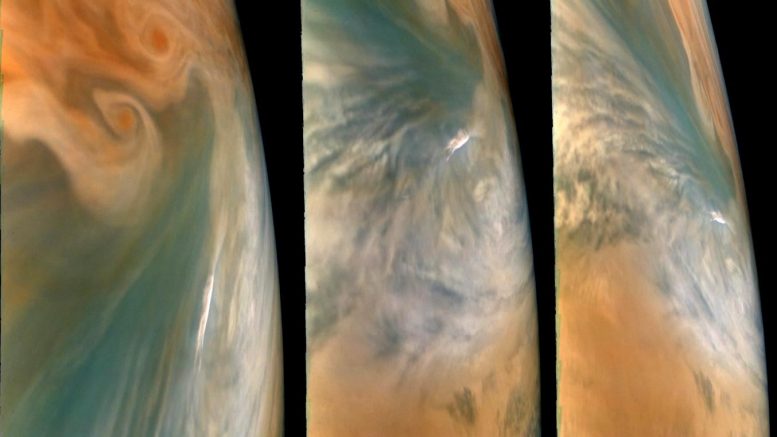

These pictures from NASA’s Juno mission present three views of a Jupiter hotspot – a break in Jupiter’s cloud deck that gives a glimpse into the planet’s deep environment. The pictures had been captured by the JunoCam imager in the course of the spacecraft’s twenty ninth flyby on September 16, 2020 on the enormous planet. Picture data: NASA / JPL-Caltech / SwRI / MSSS. Picture processing: Brian Swift © CC BY
“Large planets have deep atmospheres with no strong or liquid base like Earth,” mentioned Scott Bolton, Juno’s principal researcher on the Southwest Analysis Institute in San Antonio. “To raised perceive what is occurring deep in one in all these worlds, it’s important to look beneath the cloud layer. Juno, who just lately graduated 29th Shut-up science passport of Jupiter, does precisely that. The observations of the spacecraft make clear outdated secrets and techniques and increase new questions – not solely about Jupiter, however about all gasoline large worlds. ”
The newest long-standing puzzle that Juno has solved comes from 57 minutes and 36 seconds of data that Galileo beamed again on December 7, 1995. When the probe mirrored that its environment had been dry and windy, scientists had been shocked to attribute the discovering to the truth that the 75- The 34-kilogram probe had sunk into the environment in one in all Jupiter’s comparatively uncommon hotspots – localized atmospheric ” Deserts ”that cross the northern equatorial area of the gasoline large. Nevertheless, the outcomes from Juno’s microwave instrument present that the complete northern equatorial belt – a broad, brown cyclone band that surrounds the planet simply above the gasoline large’s equator – is usually a really arid area.
This time-lapse video clip exhibits the motion of the cyclones at Jupiter’s South Pole from February 2017 to November 2020. The data was collected with the Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument on board NASA’s Juno spacecraft. Photograph credit score: NASA /JPL-Caltech / SwRI / ASI / INAF / JIRAM
The implication is that the new spots might not be remoted “deserts,” however home windows into an enormous area in Jupiter’s environment that may be hotter and drier than different areas. Juno’s high-resolution data exhibits that these Jupiter hotspots are linked to breaks within the planet’s cloud deck and present a glimpse into Jupiter’s deep environment. In addition they present that the new spots flanked by clouds and energetic storms gas high-altitude electrical discharges just lately found by Juno and generally known as “flat lightning”. These discharges, which happen within the chilly higher reaches of Jupiter’s environment when ammonia mixes with water, are a part of this puzzle.
“Excessive up within the environment, the place flat flashes might be seen, water and ammonia mix and are invisible to Juno’s microwave instrument. A particular kind of hailstones types right here, which we name “mushballs”, ”mentioned Tristan Guillot, co-investigator with Juno on the Université Côte d’Azur in Good, France. “These mushballs get heavy and fall deep into the environment, creating a big area with a scarcity of each ammonia and water. As quickly because the mushballs soften and evaporate, the ammonia and water change again to a gaseous state and are seen to Juno once more. ”
This animation takes the viewer excessive into an awesome storm excessive in Jupiter’s environment, during which a squishy water-ammonia particle (proven in inexperienced) descends by the environment and collects water ice. The course of creates a “mushball” – a particular hailstone that consists of {a partially} liquid water-ammonia paste and a strong water-ice crust on the skin. In about 10 to 60 minutes (relying on their measurement), these mushballs attain Jupiter’s deeper layers beneath the clouds of water, the place they shortly soften and evaporate. Theoretical fashions predict that these mushballs can attain a diameter of about 10 centimeters, weigh as much as 1 kilogram and attain speeds of as much as 700 km / h on the descent. Photograph credit score: NASA / JPL-Caltech / SwRI / MSSS / CNRS
Jupiter climate report
Final 12 months the Juno staff reported on the hurricanes on the South Pole. At the moment, Juno’s instrument Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper was capturing pictures of a new cyclone that seemed to be attempting to hitch the 5 established cyclones that revolve across the large central cyclone on the South Pole.
“This sixth cyclone, the newborn of the group, appeared to alter the geometric configuration on the pole – from a pentagon to a hexagon,” Bolton mentioned. “However sadly the try failed. The child cyclone was kicked out, moved away and lastly disappeared. ”
The Juno spaceship is a dynamic engineering marvel that spins to maintain itself regular because it types oval orbits round Jupiter. Take a look at the complete interactive expertise at Eyes on the Photo voltaic System.
Presently, the staff has no agreed principle about how these large polar vortices kind – or why some seem secure whereas others are born, develop, and then die comparatively shortly. Work on atmospheric fashions continues, however at the moment no mannequin appears to clarify every little thing. How new storms happen, develop, and are both accepted or rejected is vital to understanding circumpolar cyclones, which may clarify how the environment of such large planets works usually.
Extra concerning the mission
JPL, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, administers the Juno mission for Principal Investigator Scott Bolton of the Southwest Analysis Institute in San Antonio. Juno is a part of NASA’s New Frontiers program, administered at NASA’s Marshall Area Flight Heart in Huntsville, Alabama, for the company’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. Lockheed Martin Area in Denver constructed and operates the spaceship.