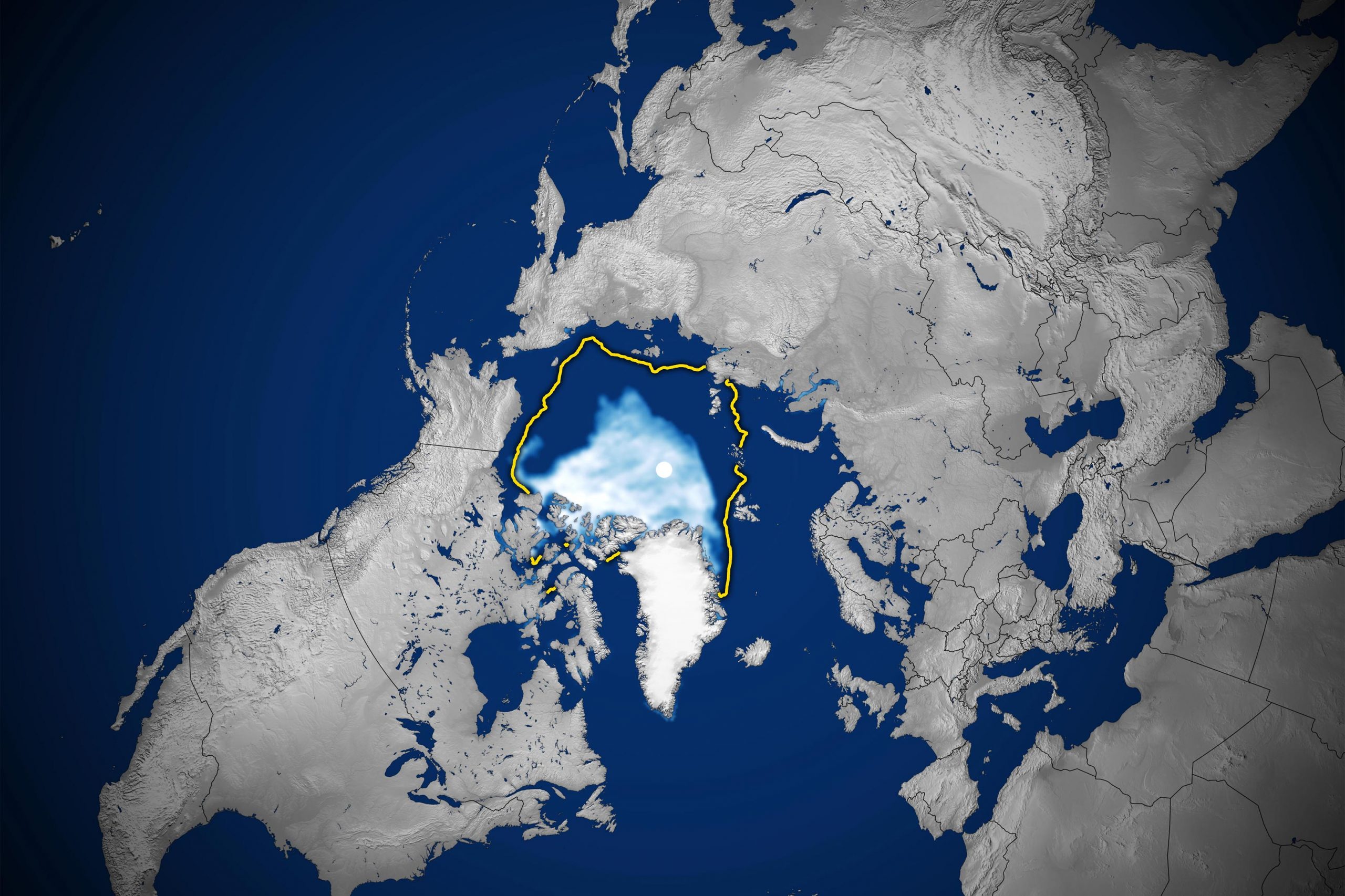
Arctic sea ice concentration, September 15, 2020.
According to researchers at, the Arctic sea ice is expected to have reached its annual minimum on September 15, 2020 NASA and the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
Analysis of satellite data showed that the Arctic ice cap shrank to 3.74 million square kilometers (1.44 million square miles), making it the second lowest recorded minimum. Experts warned that the announcement was tentative and there is still the possibility that changing winds or late-season melting could reduce ice extent.
The map at the top of this page shows the sea ice extent – defined as the total area where the ice concentration is at least 15 percent – at its 2020 minimum on September 15. The ice extent (white) on that day was far less than the average extent from 1981-2010 for the same day (yellow line). 2020 and 2012 will remain the only years when sea ice extent has fallen below 4.0 million square kilometers (1.54 million square miles).
“The minimum this year is the unsurprising result of a sustained long-term decline in Arctic sea ice,” said Alek Petty, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. The lowest 14 recorded amounts of ice have all occurred in the last 14 years.
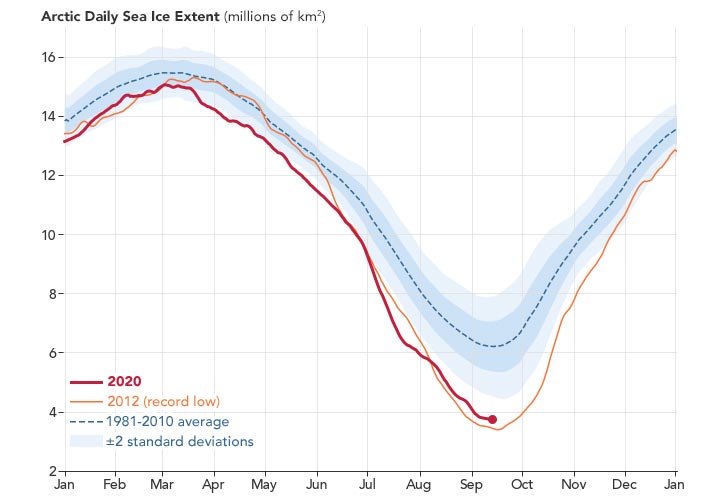
Arctic Daily Sea Ice Extent Chart, September 15, 2020.
Numerous factors contributed to the sea ice shrinking so much in 2020. In the spring, a heat wave across Siberia prepared the conditions for a rapid meltdown in the early season. In addition, the sea ice in the 2020 melting season was already much thinner than in previous years – the accumulated result of the general long-term decline in summer sea ice extent. And scientists believe warm water could work its way under the ice and melt it from below.
Weather can also affect the amount of ice in the Arctic. From late July to early August, scientists observed a low pressure atmospheric system spinning over the Arctic Ocean and wondered how this would affect the ice. A similar storm in 2012 was a major cause of the lowest recorded sea ice minimum. “The summer 2020 storm definitely had an impact, but it didn’t seem enough to push the really significant ice loss to a new record low,” said Petty.
Each year there are regional differences in air temperatures, water temperatures and weather conditions that encourage or inhibit melting in different parts of the Arctic. By the 2020 minimum date, there was even more sea ice in the Beaufort Sea than in 2012 and slightly less in the seas of Laptev and East Greenland.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Joshua Stevens using data from the National Snow and Ice Data Center. The story of Kathryn Hansen includes the coverage of Kate Ramsayer.