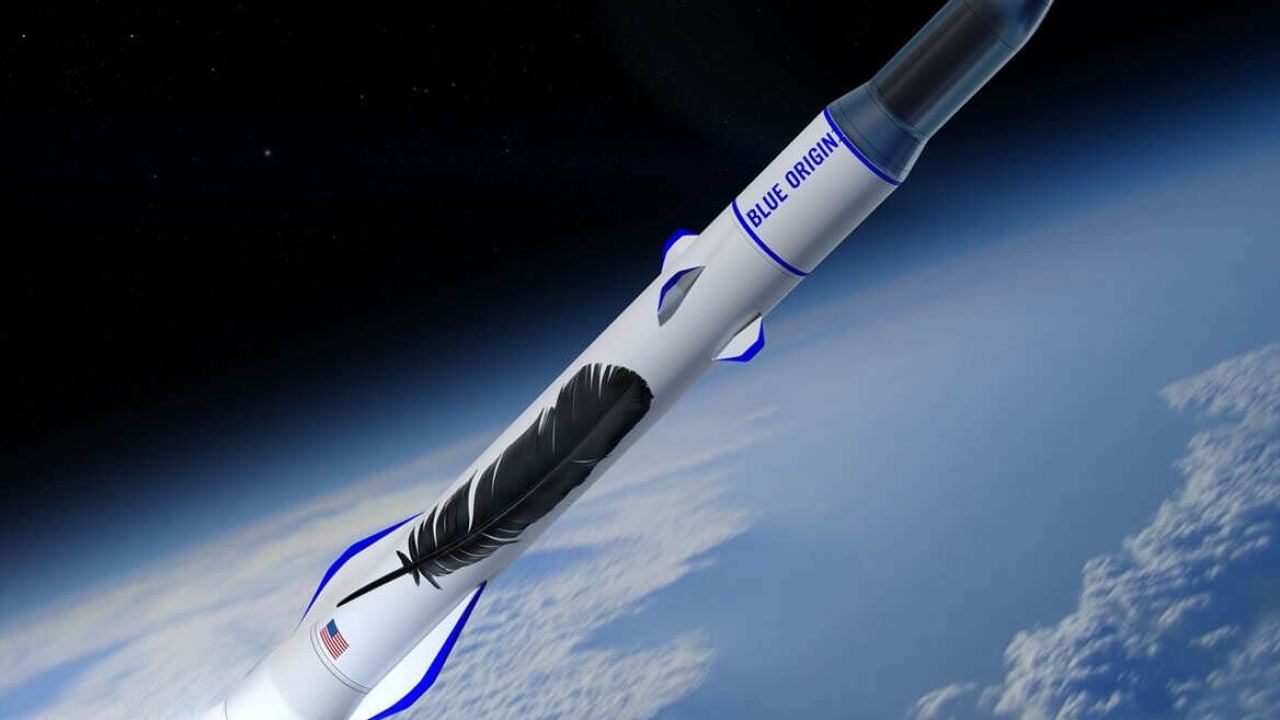
Information can be coded at the position of a particle (left or right). A demon can delete a classic bit (blue) by lifting one side until the particle is definitely on the right side. A quantum particle (red) can also tunnel under the barrier, which creates more heat. Photo credit: Professor Goold, Trinity College Dublin
Trinity researchers have discovered a unique quantum effect in information erasure that can have a significant impact on the design of Quantum computing Crisps. Their surprising discovery brings to life the paradoxical “Maxwell demon” that has plagued physicists for over 150 years.
The thermodynamics of the calculation came to the fore in 1961 when Rolf Landauer, then at IBM, discovered a connection between heat dissipation and logically irreversible operations. Landauer is known for the mantra “Information is Physical”, which reminds us that information is not abstract and is coded on physical hardware.
The “bit” is the information currency (it can be either 0 or 1) and Landauer discovered that when a bit is deleted, a minimal amount of heat is released. This is known as the Landauer limit and is the ultimate link between information theory and thermodynamics.
Professor John Goold’s QuSys group at Trinity analyzes this topic taking the quantum computer into account, erasing a quantum bit (a qubit that can be 0 and 1 at the same time).
In papers just published in the journal, Physical Examination LettersThe group discovered that the quantum nature of the information being erased can lead to large deviations in heat dissipation that traditional bit erasure does not.
Thermodynamics and Maxwell’s Demon
One hundred years before Landauer’s discovery, people like the Viennese scientist Ludwig Boltzmann and the Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell formulated the kinetic theory of gases, revived an ancient Greek idea by thinking about matter made of atoms and macroscopically derived thermodynamics from microscopic dynamics.
Professor Goold says:
“Statistical mechanics tells us that things like pressure and temperature and even the laws of thermodynamics themselves can be understood through the average behavior of the atomic constituents of matter. The second law of thermodynamics concerns the so-called entropy, which is a measure of the disturbance in a process. The second law states that without external intervention, all processes in the universe tend, on average, to increase their entropy and reach a state known as thermal equilibrium.
“It shows us that two gases at different temperatures, when mixed, reach a new state of equilibrium at the average temperature of the two. It is the ultimate law in the sense that every dynamic system is subject to it. There is no escaping: all things will reach equilibrium, including you! ”
However, the founding fathers of statistical mechanics tried from the start of kinetic theory to punch holes in the second law. Consider again the example of a gas in equilibrium: Maxwell envisioned a hypothetical being with “clean fingers” who can track and sort particles in a gas based on their speed.
Maxwell’s demon, as the creature came to be known, could quickly open and close a trap door in a box with a gas, letting hot particles pass on one side of the box but restricting cold ones to the other. This scenario seems to contradict the Second Law of Thermodynamics as the overall entropy seems to be decreasing and perhaps the most famous paradox in physics was born.
But what about Landauer’s discovery about the heat-dissipating cost of deleting information? Well, it was another 20 years before this was fully realized, the paradox resolved, and Maxwell’s demon finally exorcised.
Landauer’s work inspired Charlie Bennett – also at IBM – to investigate the idea of reversible computing. In 1982 Bennett argued that the demon must have a memory and that not measuring but erasing the information in the demon’s memory is the act that the second law restores in the paradox. As a result, computational thermodynamics was born.
New insights
Now, 40 years later, the new work of Professor Goold’s group comes to the fore, with the emphasis on the thermodynamics of quantum computation.
In the recently published article, co-published with Harry Miller of the University of Manchester and two postdocs from the QuSys Group of Trinity, Mark Mitchison and Giacomo Guarnieri, the team carefully examined an experimentally realistic erasure process that uses a quantum overlay (the qubit) enabled can be in state 0 and 1 at the same time).
Professor Goold explains:
“In reality, computers operate far from Landauer’s heat dissipation limit because they are not perfect systems. However, it is still important to think about the limit because as the miniaturization of computer components progresses, this limit is getting narrower and more relevant for quantum computers. What is amazing is that with technology these days you can really study erasure as it approaches that limit.
“We asked, ‘What difference does this clearly quantum feature make for the erasure protocol?’ And we did not expect the answer: we have found that even in an ideal erasure protocol – due to the quantum overlay – very rare events occur that give off heat that is well above the Landauer limit.
“In the work we mathematically prove that these events exist and are a unique quantum feature. This is an extremely unusual finding that could be very important for the thermal management of future quantum chips – although there is much more work to be done, especially in analyzing faster operations and the thermodynamics of other gate implementations.
“In 2020, Maxwell’s demon will continue to raise fundamental questions about the laws of nature.”
Reference: “Quantum fluctuations hinder the deletion of information with finite time near the Landauer limit” by Harry JD Miller, Giacomo Guarnieri, Mark T. Mitchison and John Goold, October 15, 2020, Physical Examination Letters.
DOI: 10.1103 / PhysRevLett.125.160602