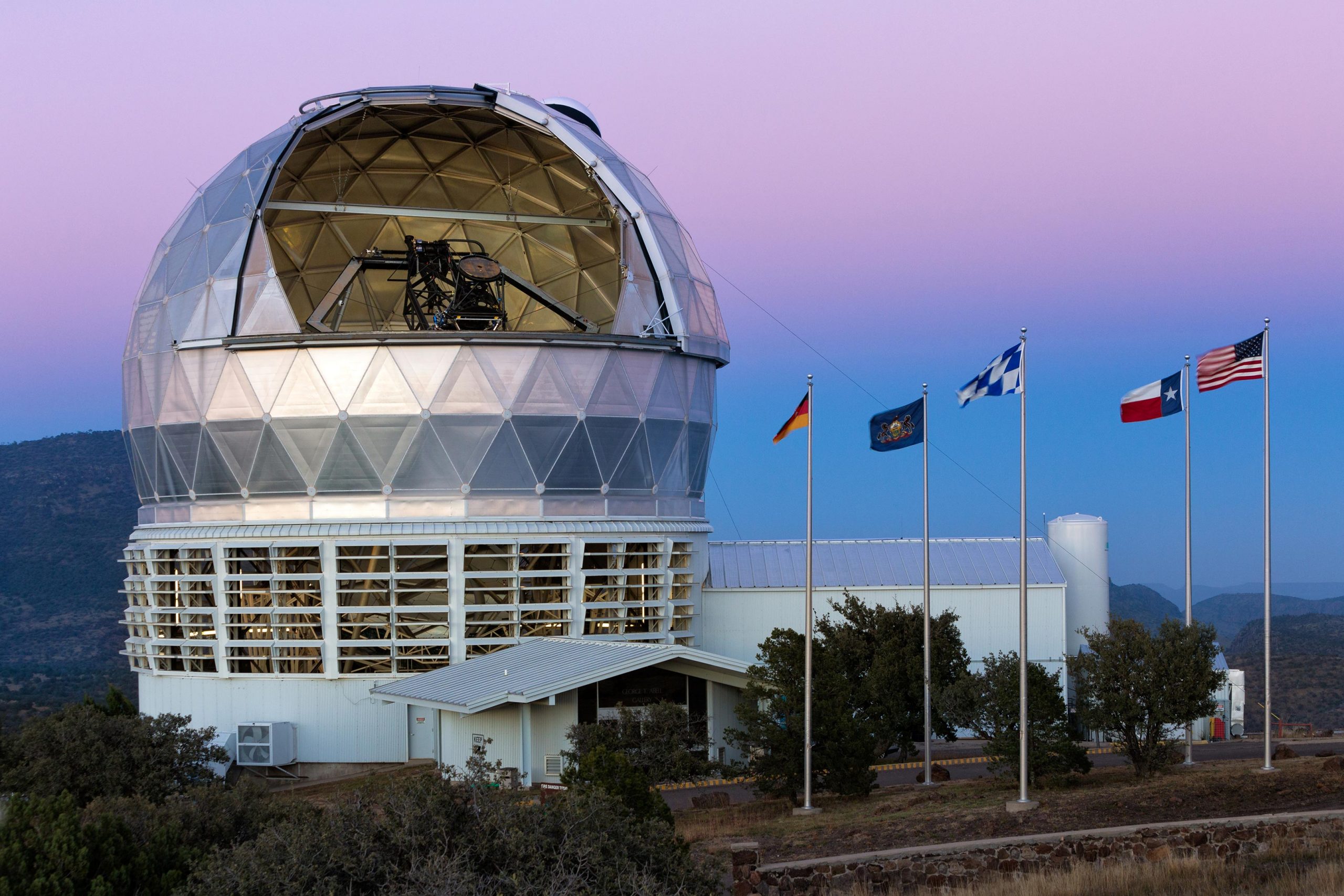
The Passion Eberly Telescope at nightfall. The flags of the 4 associate establishments fly with the US flag in entrance of the open dome. Credit score: Ethan Tweedie Images
Three years after its first check observations, the Passion Eberly Telescope Dark Energy Experiment (HETDEX) is now coaching its whole suite of devices to disclose the character and evolution of darkish vitality, the mysterious entity that’s the major part of the universe.
HETDEX, a big worldwide consortium led by the College of Texas at Austin and involving about 100 scientists, together with researchers from Penn State, plans to create one of many largest maps of the cosmos ever made. The three-dimensional map of two.5 million galaxies will assist astronomers higher perceive why the universe is at the moment increasing at an accelerating fee.
“Penn State is happy to take part on this elementary scientific investigation,” mentioned Donald Schneider, a member of the Passion-Eberly Telescope (HET) board of administrators and a distinguished professor and director of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State. “The telescope’s progressive design was created by two Penn State astronomers, Lawrence Ramsey and Daniel Weedman, and quite a few Penn State astronomers play essential roles within the observations and knowledge evaluation in HETDEX.”

The two black constructions to the left and proper of the primary mirror of the Passion Eberly telescope are nicknamed “saddlebags”. They comprise dozens of spectrographs that make up the VIRUS instrument developed for HETDEX, the Passion Eberly Telescope Experiment on Dark Energy. Credit score: Ethan Tweedie Images
HETDEX is utilizing the 10-meter HET on the McDonald Observatory in western Texas to get knowledge from two giant areas of the sky. One area is within the course of the Large Dipper, the opposite just a little southwest of the Orion constellation. Every time the telescope is aimed toward these areas, which generally take 20 minutes, HETDEX’s instrumentation information roughly 32,000 spectra and captures the cosmic fingerprint of sunshine from each object throughout the 10-meter telescope’s area of view.
“HETDEX is right here,” mentioned College of Texas astronomer Karl Gebhardt, the survey’s challenge scientist. “We’re now over a 3rd of our program and we have now this incredible knowledge set that we will use to measure the evolution of darkish vitality.”
HETDEX is a “blind” survey. As an alternative of pointing at particular targets, it information gentle from all sources over a selected sky area. These spectra are recorded over 32,000 optical fibers fed into greater than 100 devices that work collectively as a single spectrograph. This meeting, the VIRUS (Seen Integral-Subject Replicable Unit Spectrograph), is a fancy system that consists of dozens of copies of an instrument that work collectively for effectivity causes. VIRUS was specifically developed and constructed for HETDEX.
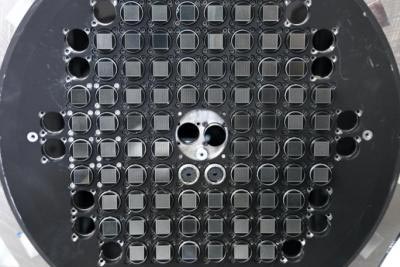
This image reveals the “focal floor” of the Passion Eberly telescope on which the optical fibers of VIRUS are organized. The circles every comprise a sq. grid of 448 fibers. When the telescope is aligned and VIRUS performs an commentary, every of the 32,000 fibers concurrently picks up a spectrum and information quite a lot of details about the velocity, course, and chemical composition of every level throughout the area of view, roughly the dimensions of the full moon. Photograph credit score: J. Pautzke / E. Mrozinski / G. Hill / HETDEX collaboration
Constructing VIRUS “was fairly a job orchestrating,” mentioned Gary Hill, an astronomer on the College of Texas and the instrument designer. “It is the most important in a variety of measures,” he mentioned, noting that it has essentially the most optical fiber in addition to a detector space like the most important astronomical cameras. VIRUS can also be an especially imposing instrument that takes up a big a part of the amount within the telescopic dome.
The HETDEX crew expects its observations to be accomplished by December 2023. In whole, the finished survey will embrace a billion spectra, “by far the most important spectral survey of all time,” mentioned Gebhardt.
“To check the properties of darkish matter and the way it evolves, we have to establish a number of million galaxies of a sure kind within the roughly one billion HETDEX spectra and map their three-dimensional distribution,” mentioned Donghui Jeong, Affiliate Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics at Penn State and head of the HETDEX science group that research large-scale constructions within the universe. “By inspecting the areas of those galaxies, we are able to examine the observations with fashions of darkish vitality and decide the affect of peculiar matter, darkish matter and darkish vitality at totally different factors within the historical past of the universe.”
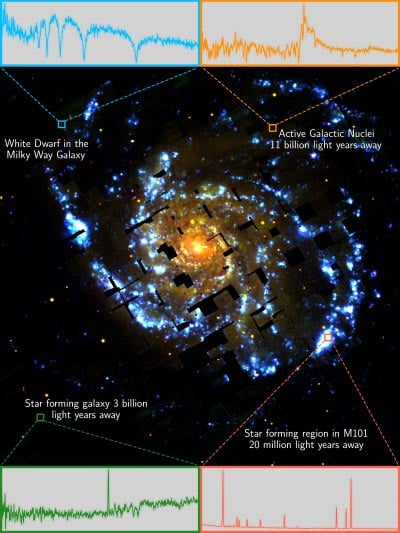

This false shade picture of the wind turbine galaxy (Messier 101) reveals the efficiency of the VIRUS instrument constructed for the HETDEX survey. The picture is a mosaic made up of the central a part of 21 VIRUS dots over a area of the sky about half the dimensions of the full moon, with some small gaps within the protection. The colours present the distinction between younger stars (blue / white) and older stars (pink / orange). The breakout packing containers solely present 4 examples of the “cosmic fingerprint” of objects on this view. Clockwise from high left: a white dwarf in our galaxy, an lively galaxy 11 billion gentle years away, a star-forming area within the windmill galaxy 20 million gentle years away, and a star-forming galaxy 3 billion gentle years away. Photograph credit score: G. Zeimann / HETDEX Collaboration
Penn State’s different HETDEX attendees embrace Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics Robin Ciardullo, Remark Supervisor for HETDEX, Analysis Professor Caryl Gronwall, and Affiliate Professor Derek Fox.
“The galaxies studied in HETDEX come from the universe’s distant previous,” mentioned Gronwall. “The gentle we uncover left these objects about ten billion years in the past when the universe was only some billion years outdated.”
Taft Armandroff, Director of the College of Texas at McDonald Observatory in Austin and Chairman of the HET Board of Administrators, commented, “HETDEX is the gathering of many astronomers and establishments to conduct the primary main examine of how darkish vitality adjustments over time . ”
HETDEX is directed by the College of Texas on the Austin McDonald Observatory and the Division of Astronomy with Penn State involvement. Ludwig-Maximilians-College Munich; the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics; the Institute for Astrophysics, Göttingen; the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics, Potsdam; Texas A&M College; The Oxford College;; the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics; The College of Tokyo; and the Missouri College of Science and Expertise.
Along with institutional assist, HETDEX is funded by the Nationwide Science Basis (grant AST-0926815), the State of Texas, the US Air Drive (AFRL FA9451-04-2-0355), and beneficiant assist from people and foundations.



