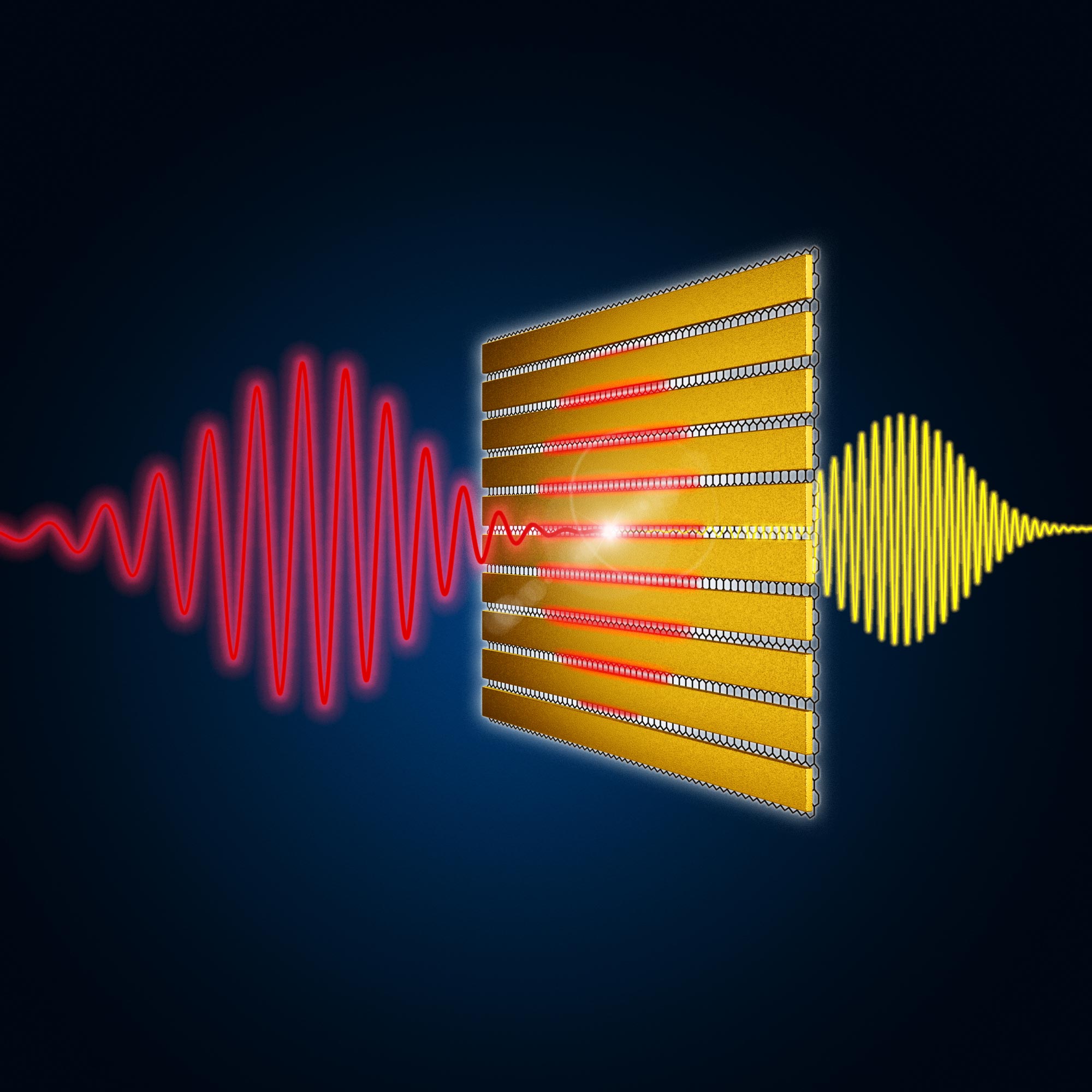
Extremely-thin gold lamellas drastically amplify the incoming terahertz pulses (purple) in the graphene layer beneath, thus enabling environment friendly frequency multiplication. Picture credit score: HZDR / Werkstatt X.
In the electromagnetic spectrum, terahertz mild is between infrared radiation and microwaves. It holds monumental potential for the technologies of tomorrow: Amongst different issues, 5G may succeed by enabling extraordinarily quick cellular communication connections and wi-fi networks. The bottleneck in the transition from gigahertz to terahertz frequencies was attributable to insufficiently environment friendly sources and converters. A German-Spanish analysis workforce with the participation of Helmholtz Heart Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) has now developed a material system with which terahertz pulses might be generated way more successfully than earlier than. It’s primarily based on Graphie a brilliant skinny carbon plate coated with a metallic lamellar construction. The analysis group introduced its leads to the journal ACS Nano.
A while in the past, a workforce of specialists at the HZDR accelerator ELBE was in a position to present that graphene can operate as a frequency multiplier: If the two-dimensional carbon is irradiated with mild pulses in the low terahertz frequency vary, these are transformed into increased frequencies. The issue to this point has been that extraordinarily sturdy enter alerts, which in flip may solely be absolutely generated by a particle accelerator, have been required to effectively generate such terahertz pulses. “That is clearly impractical for future technical functions,” explains the lead creator of the examine, Jan-Christoph Deinert from the Institute for Radiation Physics at the HZDR. “So we have been trying for a material system that additionally works with a lot much less violent enter, ie with decrease subject strengths.”
For this goal, HZDR scientists, along with colleagues from the Catalan Institute for Nanosciences and Nanotechnology (ICN2), the Institute for Photonic Sciences (ICFO), Bielefeld College, the TU Berlin and the Mainz Max Planck Institute for Polymer Analysis got here up with a New thought: The frequency conversion might be improved enormously by coating the graphene with tiny gold lamellas, which have a captivating property: “They act like antennas that significantly amplify the incident terahertz radiation in graphene,” explains mission coordinator Klaas-Jan Tielrooij von ICN2. “This offers us very sturdy fields on which the graph between the lamellas is uncovered. This permits us to generate terahertz pulses very effectively. ”
Surprisingly efficient frequency multiplication
To check the thought, workforce members from ICN2 produced samples in Barcelona: First they utilized a single layer of graphene to a glass substrate. They’ve evaporated an ultra-thin insulating layer of aluminum oxide on prime, adopted by a grid of gold strips. The samples have been then taken to the TELBE terahertz facility in Dresden-Rossendorf, the place they have been hit with mild pulses in the low terahertz vary (0.3 to 0.7 THz). Throughout this course of, the specialists used particular detectors to research how successfully the graphene coated with gold lamellae can multiply the frequency of the incident radiation.
“It labored very effectively,” stated Sergey Kovalev fortunately. He’s accountable for the TELBE facility at HZDR. “In comparison with untreated graphs, a lot weaker enter alerts have been ample to generate a frequency-multiplied sign.” Expressed in numbers, solely a tenth of the initially required subject energy was ample to look at the frequency multiplication. And with technologically related low subject strengths, the energy of the transformed terahertz pulses is greater than a thousand occasions increased due to the new material system. The broader the particular person lamellae and the smaller the uncovered graphene areas, the extra pronounced the phenomenon. Initially, the specialists have been in a position to triple the incoming frequencies. Later they achieved even larger results – 5, seven, and even 9 occasions will increase in enter frequency.
Appropriate with chip know-how
This provides a really fascinating perspective, as scientists beforehand required massive, advanced gadgets comparable to accelerators or massive lasers to generate terahertz waves. Due to the new material, it may additionally be doable to make the leap from gigahertz to terahertz with solely electrical enter alerts, ie with a lot much less effort. “Our graphene-based metamaterial can be completely suitable with present semiconductor know-how,” emphasizes Deinert. “In precept, it might be built-in into abnormal chips.” He and his workforce have confirmed the feasibility of the new course of – it could now be carried out in sure assemblies.
The potential functions might be enormous: since terahertz waves have increased frequencies than the gigahertz cellular communication frequencies used immediately, they might be used to hold way more wi-fi knowledge – 5G would grow to be 6G. The terahertz vary can also be of curiosity for different areas – from high quality management in trade to safety scanners at airports and a big quantity of scientific functions in supplies analysis.
Reference: “Lattice graph metamaterial as a platform for nonlinear terahertz photonics” by Jan-Christoph Deinert, David Alcaraz Iranzo, Raúl Pérez, Xiaoyu Jia, Hassan A. Hafez, Igor Iljakow, Nilesh Awari, Min Chen, Mohammed Bawatna, Alexey N. Ponomaryov, Semyon Germanskiy, Mischa Bonn, Frank HL Koppens, Dmitri Turchinovich, Michael Gensch, Sergey Kovalev and Klaas-Jan Tielrooij, December 11, 2020, ACS Nano.
DOI: 10.1021 / acsnano.0c08106
(operate(d, s, id){
var js, fjs = d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0];
if (d.getElementById(id)) return;
js = d.createElement(s); js.id = id;
js.src = "https://join.fb.web/en_US/sdk.js#xfbml=1&model=v2.6";
fjs.parentNode.insertBefore(js, fjs);
}(doc, 'script', 'facebook-jssdk'));