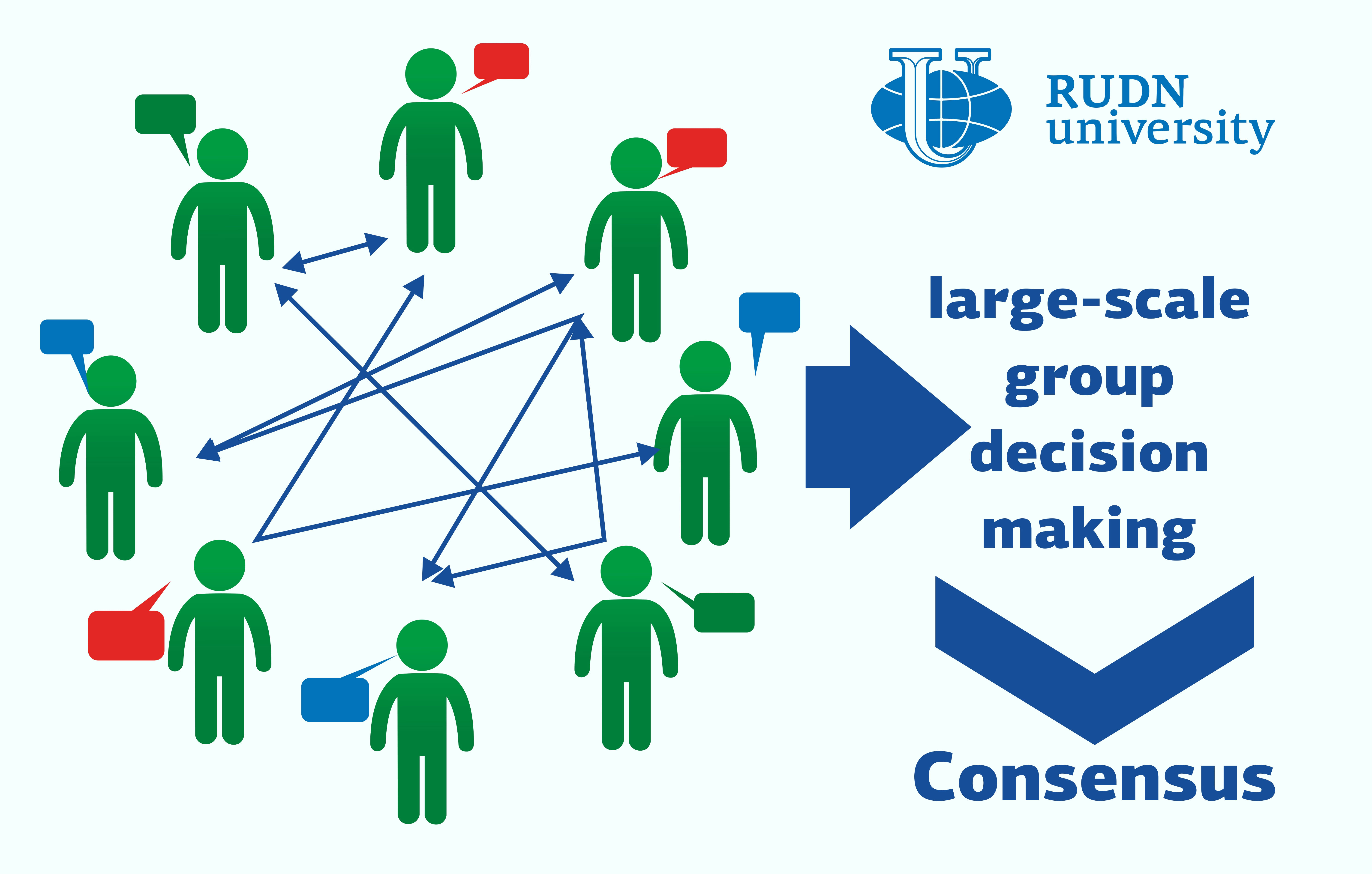
A analysis group from RUDN College developed an algorithm that permits giant teams of individuals to make optimum choices in a quick time. They confirmed the effectivity of their mannequin utilizing the instance of the market the place the COVID-19 outbreak started. The mannequin helped administration and sellers agree to shut the market and attain consensus on the extent of compensation in simply three steps. Photograph credit score: RUDN College
A analysis group from RUDN College developed an algorithm that permits giant teams of individuals to make optimum choices in a quick time. They confirmed the effectivity of their mannequin utilizing the instance of the market on which the outbreak of COVID-19 began. The mannequin helped administration and sellers agree to shut the market and attain consensus on the extent of compensation in simply three steps. An article concerning the algorithm was printed within the Data science Diary.
Decision principle is an space of arithmetic that research the patterns of decision making and technique choice. In mathematical phrases, decision making is a multi-criteria optimization process. Professional opinions, judgments and doable dangers are thought of as variables, and the relationships between contributors and the seek for an optimum answer are expressed as mathematical operations. LSGDM is a mannequin in decision principle that describes decision-making conditions with over 20 contributors on the skilled degree. Your opinions are influenced by private relationships: for instance, associates assist one another’s views. This will increase uncertainty because it turns into harder to persuade contributors and attain consensus. A analysis group of mathematicians from RUDN College proposed a methodology to take away this uncertainty.
“Because of right this moment’s technological developments, increasingly individuals are beginning to take part in decision-making processes. For that reason, LSGDM has turn into a sizzling matter for researchers. In LSGDM, the contributors characterize totally different areas of curiosity and due to this fact it takes longer to succeed in consensus. The method requires a moderator who can persuade all events to alter their thoughts, ”mentioned Prof. Enrique Herrera-Viedma, head of the analysis group at RUDN College.
The answer proposed by his group of mathematicians is predicated on the so-called strong optimization method. It’s utilized to optimization duties which can be delicate to modifications within the preliminary dates (on this case, the non-public relationships between contributors). The mathematicians proposed a new method of dividing consultants into clusters primarily based on the power of relationships and the extent of belief between them. The algorithm consisted of a number of steps. First, the consultants had been grouped collectively; Then the group recognized a cluster with the opinion that differed most from the collective judgment. and after that this opinion was corrected. The iterations had been repeated till all contributors had agreed on a answer. The strategies of correction of opinion had been irrelevant from a mathematical perspective. The one issue that mattered was the price of negotiation per unit: the quantity of assets (time, cash, and so on.) that needed to be expended to realize the specified final result.
The analysis group utilized the mannequin to a real-life instance. A fish market in Wuhan needed to shut following the COVID-19 outbreak. The administration was on the lookout for an optimum answer: It needed to compensate the sellers’ losses whereas staying inside the market price range. The mathematicians chosen 20 salespeople who requested numerous quantities of compensation for closing their cubicles: 200 to 900 yuan. Members had been divided into 4 clusters primarily based on elements similar to related opinions, the proximity of the stands to at least one one other, and so forth. With the algorithm proposed by the group, sellers and directors can attain consensus in simply three steps. The ultimate quantity of compensation was 880 yuan, and the market administration negotiating value was discovered to be the bottom in comparison with different present fashions.
Reference: “Consensus on the decision-making of enormous teams in social networks: The minimal value mannequin primarily based on strong optimization” by Yanling Lu, Yejun Xu, Enrique Herrera-Viedma and Yefan Han, August 29, 2020, Data science.
DOI: 10.1016 / j.ins.2020.08.022
(operate(d, s, id){
var js, fjs = d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0];
if (d.getElementById(id)) return;
js = d.createElement(s); js.id = id;
js.src = "https://join.fb.web/en_US/sdk.js#xfbml=1&model=v2.6";
fjs.parentNode.insertBefore(js, fjs);
}(doc, 'script', 'facebook-jssdk'));